- Welcome to Simply Fortran
- Purchasing and Activating Simply Fortran
- Using Simply Fortran
- The Simply Fortran Interface
- Editing in Simply Fortran
- Projects in Simply Fortran
- Building Projects
- Launching Projects
- Debugging Programs
- External Tools
- Version Control
- Options and Configuration
- Licensing
Appearance and Behavior Options
The Appearance and Behavior Options window allows the user to configure the look and feel of Simply Fortran and the features of its editor. Because many users have Simply Fortran installed on multiple machines, the Import Settings and Export Settings buttons can be used to save these settings to a file and load them into Simply Fortran from these files respectively to maintain consistent appearance and behavior settings on multiple machines.
The options are divided into tabs, each described below:
Appearance
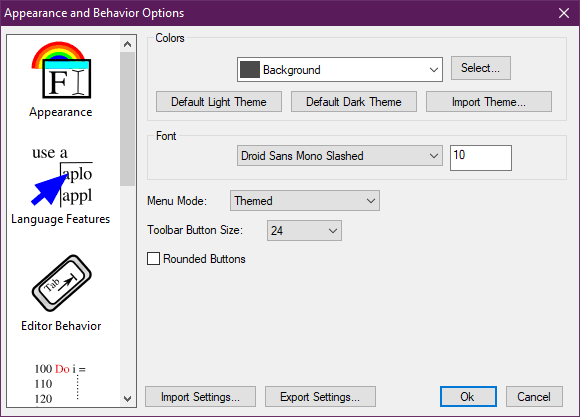
The colors utilized by the editor can be modified by the user. A drop-down box specifies which color component to change, and the Select… button opens a selection dialog. Because Simply Fortran features syntax highlighting, the user can configure keywords, comments, and variables to stand out from each other.
The default light and dark theme buttons will set the editor colors to sensible light and dark colors respectively.
Under the colors drop-down, an Import Theme… button allows the user to select and import Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio 2010-2013 color themes.
The font selection dropdown and the associated size text box allows the user to adjust the fonts used in Simply Fortran. The font size may also be increased in real-time within the editor by holding the Control key while moving the mouse’s scroll wheel.
The menu mode option allows the user to switch between themed, custom menus to match the overall Simply Fortran theme and system menus that rely on Windows for management and drawing.
The toolbar button size option can change the size of toolbar buttons throughout Simply Fortran.
Enabling rounded buttons will cause some buttons in Simply Fortran to appear slightly rounded, which is the default on Windows 11. When this setting is changed, Simply Fortran must be restarted to take effect.
Language Features
These options enable and disable certain Simply Fortran features within the editor related to enhancing productivity while working with known source languages . Note that this panel may scroll to reveal additional options.
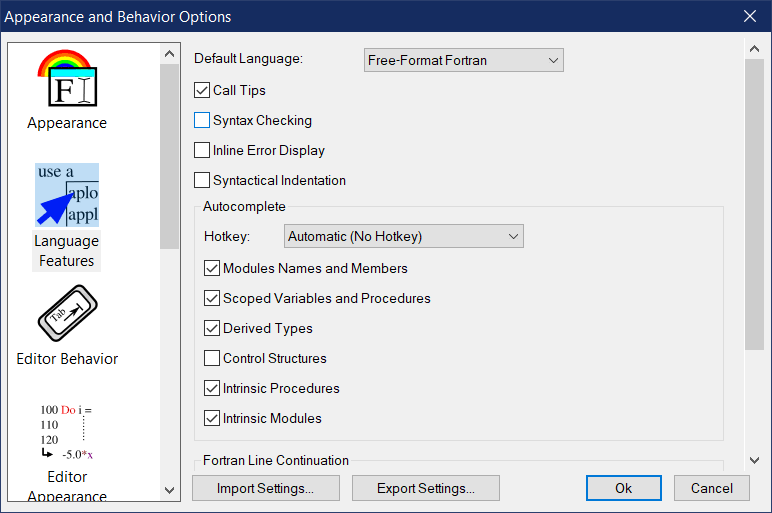
Default Language
This option reflects the default language and syntax highlighting to be used when a new file is opened in the editor. Normally, Simply Fortran will determine the syntax highlighting method to use based on the file name. However, when a new editor is opened without a pre-existing file, this option will allow the editor to default to free-format Fortran, fixed-format Fortran, or plain text (None).
Call Tips
When a source file in a supported language is being edited, the editor can optionally display real-time help for both intrinsic and user-defined procedures and functions. Enabling this option will allow help boxes to appear when a Fortran intrinsic procedure is entered followed by an opening parentheses.
Syntax Checking and Inline Error Display
These two related options control real-time syntax checking within an editor tab. For a supported language , syntax checking allows Simply Fortran to periodically process code within the editor to check for warnings or errors. Errors or warnings will then be underlined appropriately within the editor. Enabling Inline Error Display will also display the error and warning messages directly in the code.
Syntactical Indentation
Enabling this option allows Simply Fortran to intelligently indent or dedent code whenever a subunit of code in the file’s particular language is entered or exited. For example, if Simply Fortran detects the beginning of a loop in the code after ENTER is pressed, the next line will be automatically indented one tab width deeper than the loop’s beginning line. Conversely, if the end of a loop is detected after ENTER is pressed, Simply Fortran will dedent both the current line and the loop’s closing statement (if applicable) to match the indentation of the loop’s opening statement.
Autocomplete
The Autocomplete options control which types of autocompletion popups Simply Fortran will provide while typing. The four types of supported completion are listed below:
- Modules Names and Members – When use is entered, a popup will display all known module names. If followed by the only specifier, a popup will display any known members of the module.
- Scoped Variables and Procedures – When typing any code, popups will appear suggesting variables and procedures currently known to be visible within the current program or subprogram.
- Derived Types – If a % symbol is entered after variable known to be a derived type, a popup will suggest any members of the derived type.
- Control Structures – A popup will provide common suggestions to follow an end statement.
- Intrinsic Procedures – A popup will provide Fortran intrinsics as suggestions.
- Intrinsic Modules – Module names that are part of the Fortran standard will be suggested when appropriate.
All autocompletion modes are supported when editing Fortran. Python and C support some autocompletion via the Scoped Variables and Procedures option.
By default, Simply Fortran will always attempt to show autocompletion suggestions. The Hotkey option allows the user to change this behavior such that the autocompletion suggestions will only appear if the selected hotkey is pressed while typing.
Fortran Line Continuation
Simply Fortran can optionally and automatically syntactically wrap Fortran code when a certain column is reached while typing. When enabled, by default, code will be wrapped at the 132nd column for free-format Fortran, and at the 72nd column for fixed-format Fortran. This automatic continuation will attempt to split the code line at an appropriate location, insert the correct continuation markers, and indent the subsequent line.
Alternatively, the user may wish to use line continuation that is different from Fortran’s maximum line length limits. The “Force Continuation at Custom Column” checkbox and entry can be used to set a custom column that might be more visually appealing than Fortran’s limits.
Editor Behavior
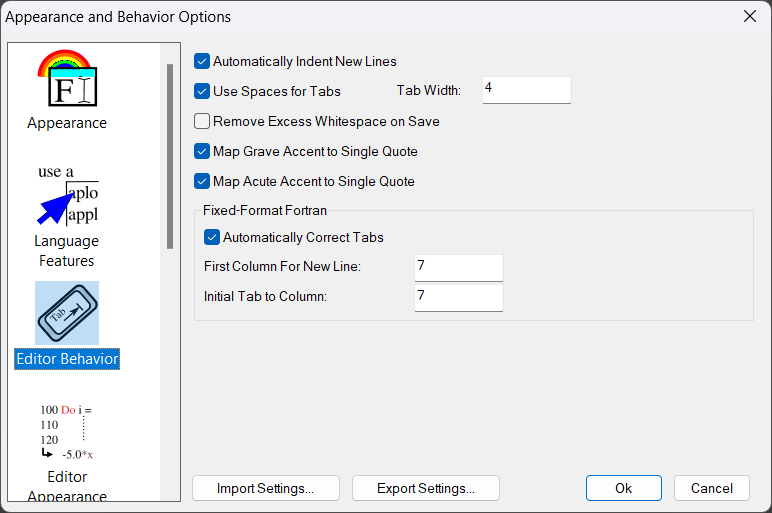
This panel controls stylistic editing options, as described below:
Automatically Indent New Lines
When enabled, a new line will be automatically indented to match the indent level of the previous line.
Use Spaces for Tabs
When the tab key is pressed, Simply Fortran normally introduces a true tab character into the text. If this option is enabled, however, an equivalent number of spaces is added rather than the tab character.
If the editor is currently in “Makefile” mode, i.e. the user is editing a Makefile, this option will be ignored, and true tab characters will be used.
Tab Width
The tab width specifies the size of either the tab character in the editor or the equivalent number of spaces if the Use Spaces for Tabs option is enabled.
Remove Excess Whitespace on Save
When enabled, any trailing whitespace on lines is stripped prior to writing the file to disk.
Map Grave Accent to Single Quote and Map Acute Accent to Single Quote
The grave and acute accents, which are sometimes readily available on certain keyboards, are angled to encompass text. The Fortran language, however, only accepts the apostrophe character as a valid single-quote character. To avoid confusion, these two accent characters can be mapped to an appropriate character that the Fortran compiler will recognize as a valid single quote when typed. These options only trigger when typing; paste operations or loading a file are unaffected by these options.
Fixed-Format Fortran Specific Behavior
Because fixed-format Fortran represents a somewhat special case in programming due to its significant leading whitespace, additional options are provided to streamline fixed-format programming.
Automatically Correct Tabs
When this option is enabled, fixed-format Fortran and Fortran source code conforming to Fortran 77 and earlier standards will be scanned for leading tabs and corrected automatically when loaded into an editor. Tabs were common in shifting code past the sixth column in fixed-format Fortran, but this methodology does not conform to Fortran standards.
First Column for New Line
When auto indentation is disabled above or a prior line contained a comment or line number label, the programmer often wants the next line to begin on the seventh column in fixed-format programming. This option allows the user to specify this column explicitly to avoid always starting in the first column, which is not as common in fixed-format programming.
Initial Tab to Column
Any tab keypresses prior to the column specified should move the cursor immediately to this specified column.
Editor Appearance
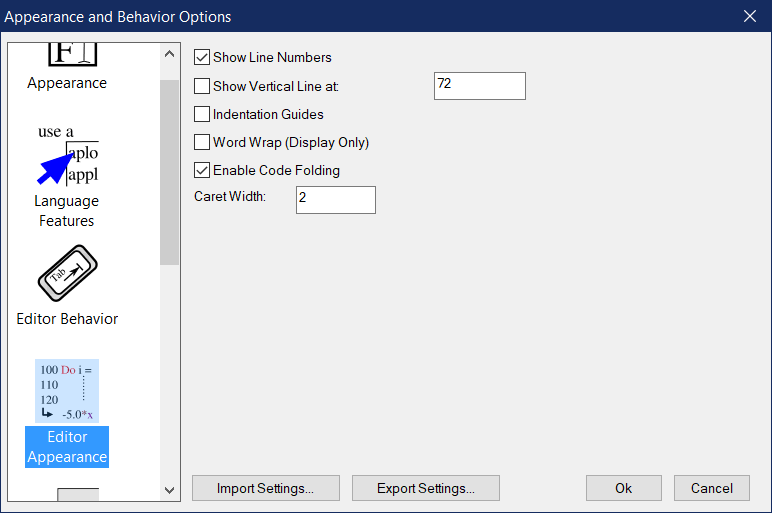
Options on this panel control the appearance of the editor (excluding colors and fonts).
Show Line Numbers
Enabling this options activates a line number listing for files in the editor.
Show Vertical Line
Displaying a vertical line is useful for determining when a single line of text is approaching a limit. For example, the Fortran 90 standard dictates that the maximum length of a single line is 132 characters. Enabling this guide can make development easier.
Indentation Guides
Indentation guides are useful in lining up indented text within a Fortran source file. In the case of large loops, for example, where the loop contents are indented, the guide can be used to determine where the dedented loop closing should be place.
Word Wrap
Enabling this option causes lines wider than the editor tab to wrap to the next line. However, this wrapping is performed for display purposes only; it is not reflected in the saved file. When a line does wrap, a small arrow will appear on subsequent display lines to indicate that they are actually continuations of the previous line.
Enable Code Folding
Code folding in the editor is depicted as small bars in the editor’s margin. When bars are clicked and this option is enabled, code structures (conditionals, loops, procedures, etc.) can be collapsed to a single line while editing. This behavior can be helpful when editing code surrounding long, embedded control structures.
Caret Width
This number specifies the width of the text cursor within the editor tab. This number can be either 1, 2, or 3, with 3 being the thickest.
Tab Behavior
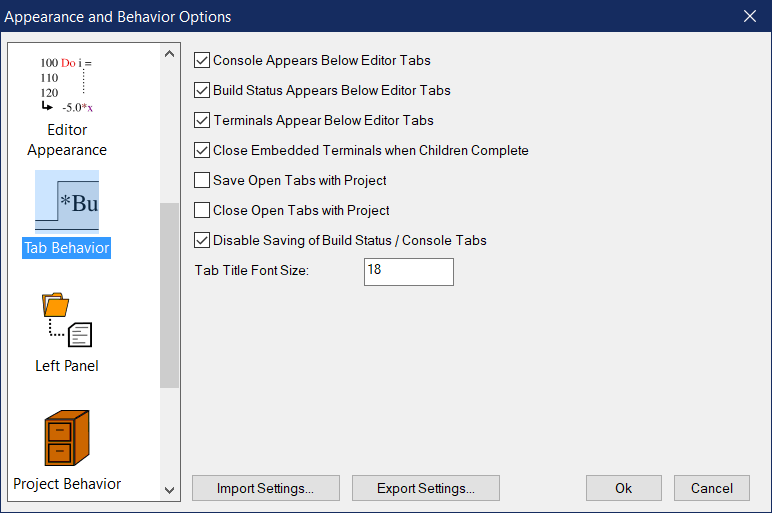
Options in this panel control the behavior of editor, build status, and console tabs.
Console Appears Below Editor Tabs
Enabling this option directs Simply Fortran to open the internal Console tab at the bottom of the window below other editor tabs.
Build Status Appears Below Editor Tabs
Enabling this option directs Simply Fortran to open the Build Status tab at the bottom of the window below other editor tabs.
Terminals Appear Below Editor Tabs
Enabling this option directs Simply Fortran to open any terminals requested at the bottom of the window below other editor tabs.
Close Embedded Terminals when Children Complete
If enabled, terminal panels will close when the child process completes. For example, if a simple shell is running, typing “exit” will cause the terminal tab to close.
Save Open Tabs with Project
When enabled, the files from a project that are currently opened and their positions within the Simply Fortran window are stored in the project file. When the project file is later opened, Simply Fortran will automatically open and position these tabs again.
Close Open Tabs with Project
If enabled, unmodified editor tabs that contain files belonging to the project being close will also be closed. Any files with changes will remain open regardless of this feature’s status.
Disable Saving of Build Status / Console Tabs
This options, when checked, causes Simply Fortran to ignore Save and Save As commands in the main menu, toolbar, or the corresponding hotkeys when the Console or Build Status tab is the current tab. This feature is present to reduce the posibility of mistakenly overwriting Fortran source code when the current tab isn’t obvious. The Console and Build Status tabs can still be saved when this is enabled by right-clicking on the tab itself and selecting the appropriate item.
Tab Title Font Size
This value specifies the font size displayed in editor tab titles only. The font size within the editor is specified in the Appearance section.
Left Panel
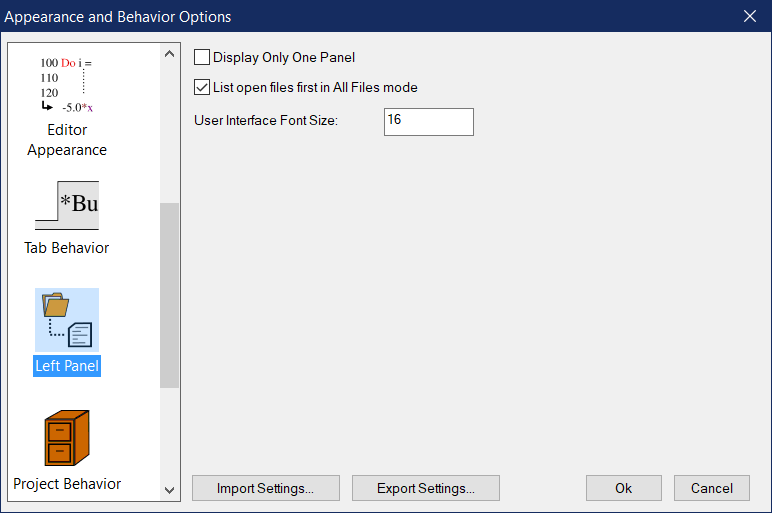
Options in this section control the appearance and behavior of Simply Fortran’s left panel where auxiliary information about projects, files and debugging are normally displayed.
Display Only One Panel
This option limits the left region of Simply Fortran to show a single panel at a given time. Enabling it may be useful if the behavior of pre-3.0 Simply Fortran is desired or if vertical screen height is limited.
List open files first in All Files mode
When enabled, the Project Outline will, in All Files mode, list open files at the top of the known files list. These filenames will appear bold as well.
User Interface Font Size
This setting specifies the size of the fonts used in all panels.
Project Behavior
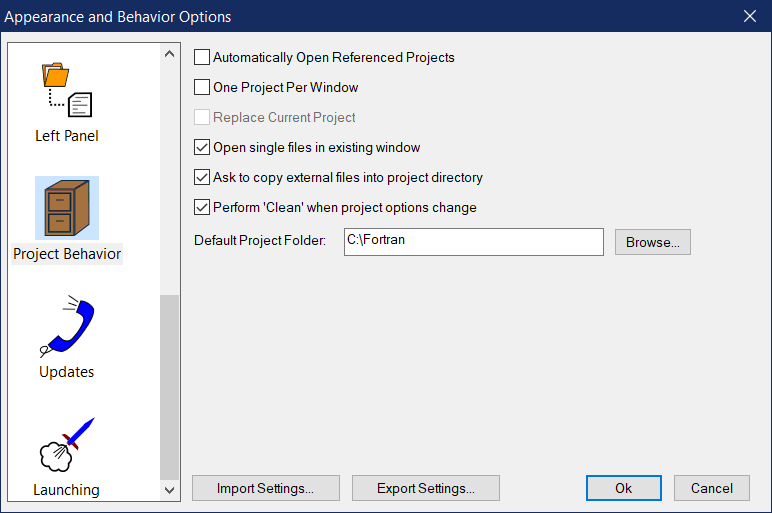
This panel controls how Simply Fortran loads and deals with projects. If the user needs to change the options of a particular project, the Project Options window should be opened.
Automatically Open Referenced Projects
When enabled, any projects referenced by a project being opened will also be opened in the same window. The referenced projects are always opened in the same window regardless of other settings on this panel via this option.
One Project Per Window
Enabling this option limits Simply Fortran to a single project per window. If a second project is opened, a new window will be opened or the current project will be replaced depending on the final option.
Replace Current Project
If Simply Fortran is limited to one project per window, enabling this feature will cause the current project to be closed when a new project is opened rather than opening a new Simply Fortran window.
Open Single Files in Current Window
When enabled, single Fortran files that are requested to be opened by the operating system by Simply Fortran should open in the existing, open window rather than starting another instance of Simply Fortran.
Ask to Copy External Files into Project Directory
This option will ask the user, whenever a file is added to a project that is not in the project directory or a subdirectory of the project directory, if the user wishes to copy the file from its current location into the current project directory.
Perform Clean When Project Options Change
When this option is enabled, changing project options at any time via the Project Options window will cause Simply Fortran to perform Clean operation on the current project. This feature ensures any changed project options will be applied to all source files, avoiding the situation where pre-existing object files do not currently reflect the new project options.
Default Project Folder
This option allows the user to specify the directory where Simply Fortran will place new projects by default when creating a new project.
Updates
This category controls Simply Fortran’s checking for version updates. Simply Fortran, by default, will contact a server to determine if there is a newer version available. If enabled, the software will notify the user in the main window’s status bar.
Check for Updates at Start
When Simply Fortran starts, it can optionally contact a server to see if a newer version is available. This can be disabled if, for example, you wish to lock Simply Fortran to the current version.
Check for Updates Now
Clicking this button will check if a new version is available immediately.
Launching
This category contains options related to how Simply Fortran spawns child processes, including programs compiled by the user.
Use Resilient Process Creation
Enabled by default, this option uses a background launch system that will timeout if the child process is not started after 30 seconds. This timeout period is needed to warn the user if, for example, a virus scanner is intercepting and blocking the process creation calls.
Force Launch Using system() Call
This option will launch projects using the system() library call rather than the normal execl() method on Linux and macOS, which can be problematic in certain conditions.
Detect Crashes and Suggest Diagnostics and Debugging
When enabled, Simply Fortran will attempt to detect your program crashing after launch. When a crash is detected, Simply Fortran will suggest enabling Runtime Diagnostics or launching the program within the debugger if possible. This feature is meant to aid users in quickly hunting down crashes if they are unfamiliar with some of Simply Fortran’s capabilities.
Terminal
This category, available on Windows, controls the behavior of the built-in Terminal.
Terminal Command Interpreter
This option allows the user to switch between Windows Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell as the command interpreter to be used when a terminal is opened in Simply Fortran.